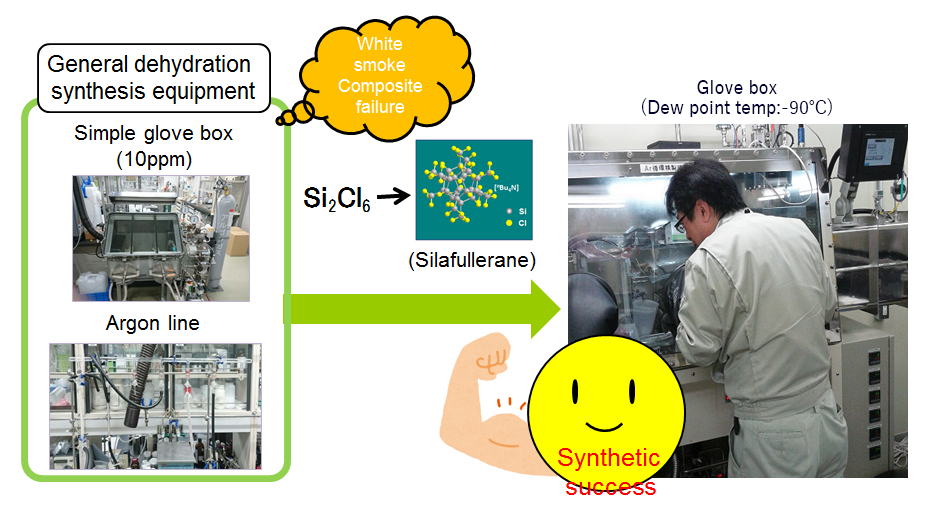
We propose next-generation material related development through development of KRI owned basic technology.
Synthetic environment provided by KRI
- ●With nonaqueous secondary battery materials such as lithium, magnesium, sodium, it could be possible to promote efficient development by eliminating the influence of water during synthesis.
- ●Isolation of unstable complexes and synthesis of synthetic intermediates can lead to elucidation of reaction mechanism.
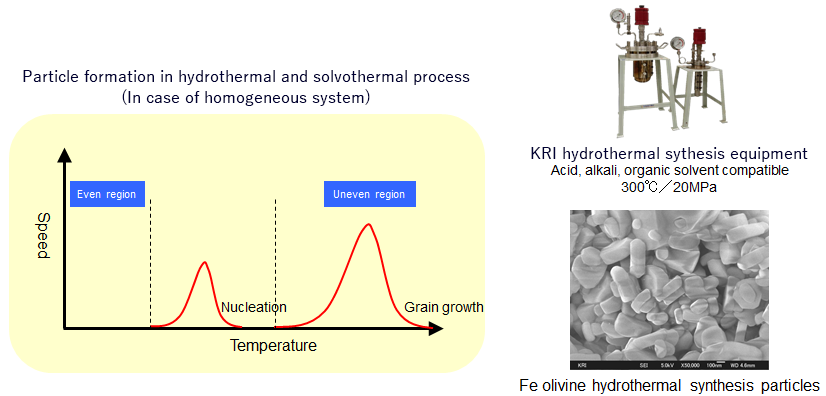
Fabrication process technology of next generation materials
After nucleation from a homogeneous system, it shifts to a heterogeneous reaction system.
Uniform particles can be obtained by appropriately selecting the transition conditions at this time.
Nanocoating
●Introduction of tumbling fluid bed granulator dryer / coater system
- ・KRI newly introduces tumbling fluid bed granulator dryer / coater system. It enables nanocoating with more precise and mass production not possible with conventional sol-gel method.

●Fusion with KRI coating technology
- ・Utilizing the knowledge of the sol-gel method, it develops into a tumbling fluid bed granulator dryer / coater system (coating material, quantity, form, etc.).
- ・Not only inorganic compounds, but also nanocoating of organic materials (polymers, etc.) are also possible.
●Expected performance by nanocoating
- ・Improvement of battery performance by nanocoating on positive and negative electrode material surface (charge / discharge cycle deterioration, input / output characteristics, gas generation, etc.)
- ・Ionic conductivity improvement and reaction suppression by nanocoating on solid electrolyte
- ・Analysis of material surface structure on battery performance

●NMR:Environment for battery related evaluation
- ・Sampling and measurement without exposing materials to atmosphere
- ・Low temperature measurement up to -100℃
- ・PFG-NMR (Molecule diffusion measurement)
[Analysis example]
- ・Solid state NMR low temperature measurement: analysis of lithium insertion state
- ・Electrolyte analysis by molecular diffusion measurement

●XRD: Structural analysis by multifunctional X-ray diffractometer
- ・Structural changes can be traced at temperature variables (−40℃~800℃)
- ・Atmosphere controllable
- ・Tracking crystal structure change in charge / discharge state
- ・Detection of trace impurities in active materials
[Analysis example]

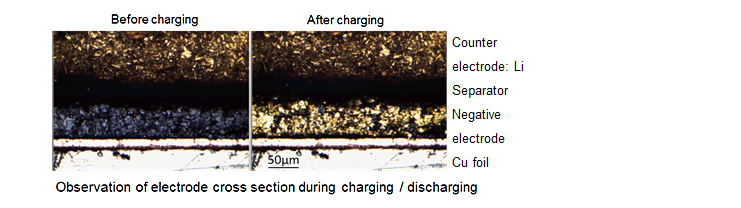
●Confocal microscope: Electrode cross section change (Operando measurement)
- ・Observation of electrode cross section during charge / discharge (particle: electrode thickness)
- ・Observation of dendrite deposition sites
- ・Observation of uneven reaction in electrodes
- ・Measurement at −30℃~80℃ is possible